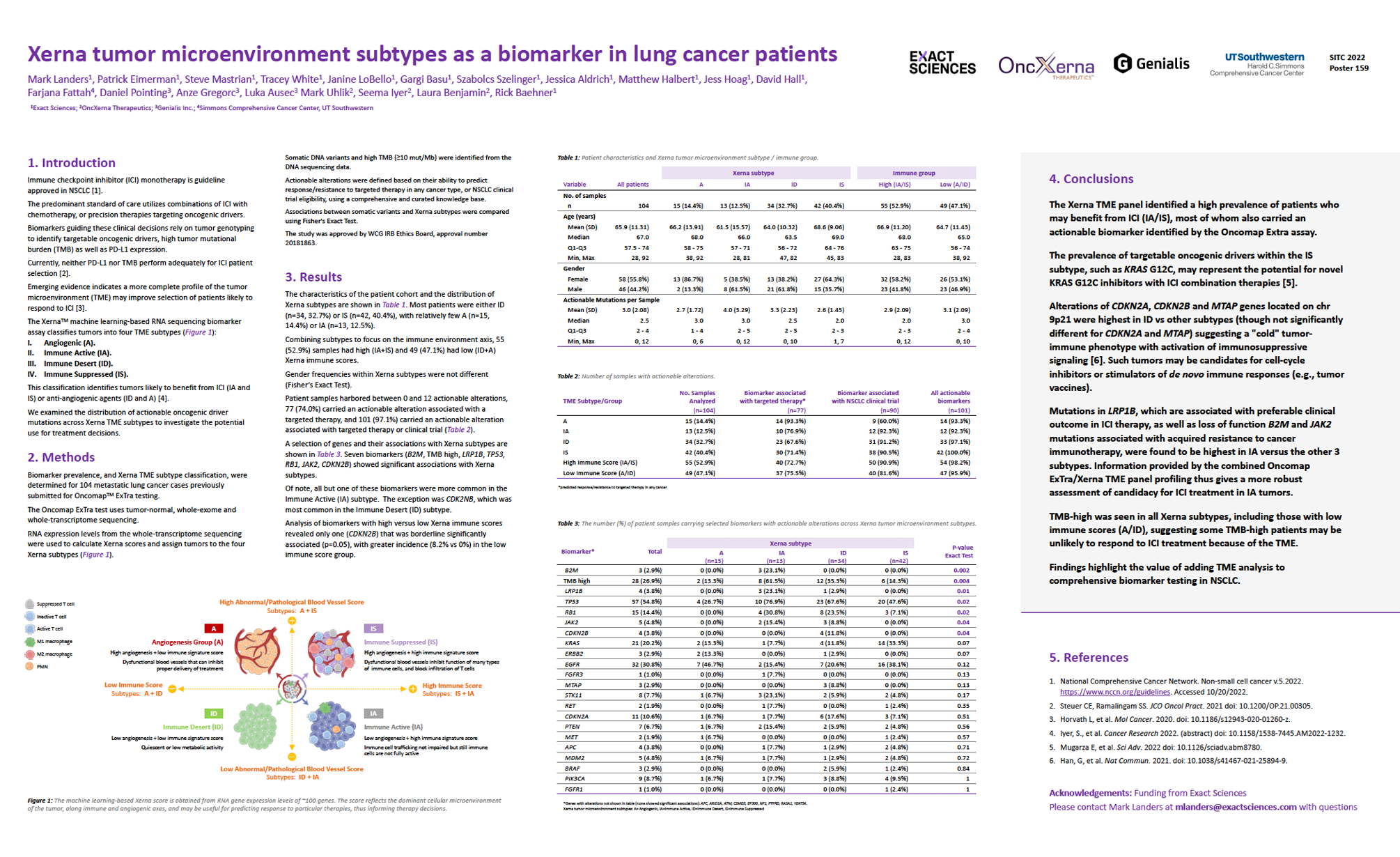
This study investigates the potential of the Xerna™ TME panel, a machine learning-based RNA sequencing assay, to predict the benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The panel classifies tumors into four subtypes based on tumor microenvironment (TME): Angiogenic (A), Immune Active (IA), Immune Desert (ID), and Immune Suppressed (IS). Analysis of 104 NSCLC samples revealed significant associations between TME subtypes and actionable mutations, suggesting that the Xerna TME Panel in predicting response to immune checkpoint inhibition, and concluded that it compares favourably with existing biomarkers such as the tumor mutational burden (TMB). Adding this assay to a host of other tests in Exact Sciences’ Oncomap ExTra platform now enables researchers and clinicians to make more informed clinical decisions.
Published at SITC 2022.
Mark Landers1, Patrick Eimerman1, Steve Mastrian1, Tracey White1, Janine LoBello1, Gargi Basu1, Szabolcs Szelinger1, Jessica Aldrich1, Matthew Halbert1, Jess Hoag1, David Hall1, Farjana Fattah4, Daniel Pointing3, Anže Gregorc3, Luka Ausec3 Mark Uhlik2, Seema Iyer2, Laura Benjamin2, Rick Baehner1
1 Exact Sciences
2 OncXerna Therapeutics
3 Genialis Inc.
4 Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center, UT Southwestern